With decimal place value chart printable at the forefront, embark on a journey of discovery as we unravel the mysteries of decimal numbers. Prepare to be amazed as we explore the significance of each digit in a decimal number and how the chart aids in arithmetic operations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the decimal place value system, learn how to read and write decimal numbers using the chart, compare and order them, and even perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with ease. Get ready to master the art of decimals with the help of our handy printable chart.
Introduction to Decimal Place Value Chart
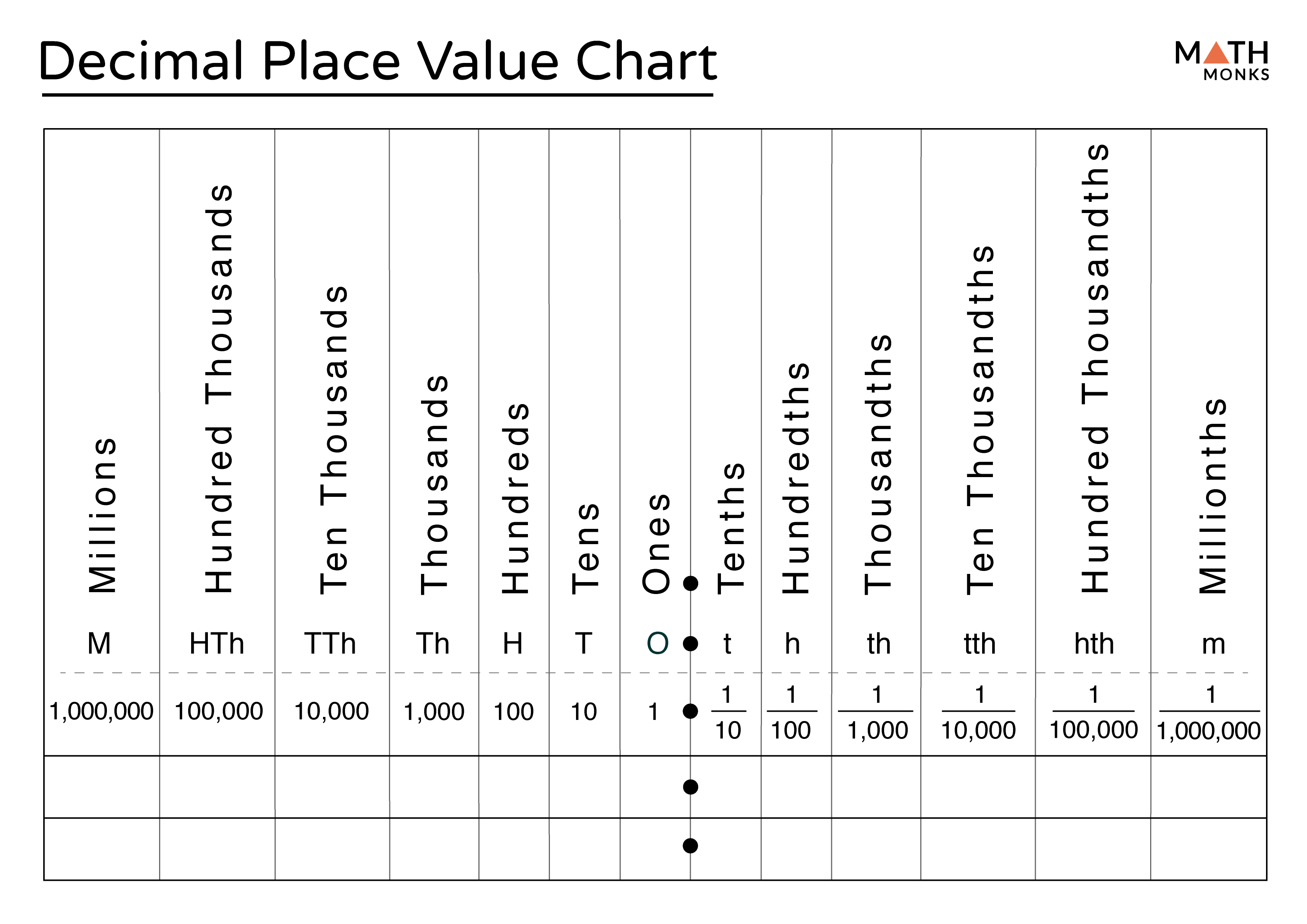
A decimal place value chart is a visual representation of the value of each digit in a decimal number. It is important in understanding decimal numbers as it helps us determine the position and significance of each digit.In a decimal place value chart, each digit is assigned a specific place value based on its position.
The rightmost digit represents the ones place, followed by the tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on. The value of each digit is determined by multiplying it with the corresponding place value.For example, in the decimal number 0.325, the digit 5 is in the ones place, the digit 2 is in the tenths place, and the digit 3 is in the hundredths place.
The value of 5 is 5 x 1 = 5, the value of 2 is 2 x 0.1 = 0.2, and the value of 3 is 3 x 0.01 = 0.03.Decimal place value charts can be represented in different formats.
One common format is a table with columns representing the place values and rows representing the digits. Each cell in the table contains the value of the digit based on its place value.The decimal place value chart is particularly useful in performing arithmetic operations with decimals.
It allows us to align the digits based on their place values, making it easier to add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals accurately.
Examples of Decimal Place Value Charts
- Decimal Place Value Chart:
| Place Value | Digit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Ones | 2 | 2 |
| Tenths | 5 | 0.5 |
| Hundredths | 3 | 0.03 |
By using a decimal place value chart, we can easily determine the value of each digit in a decimal number and perform arithmetic operations accurately.
Understanding the Decimal Place Value System
The decimal place value system is a way of representing numbers using a base of 10. In this system, each digit’s position in a number determines its value. The value of a digit is determined by its position relative to the decimal point.For
example, in the number 245.78, the digit 5 is in the ones place, the digit 4 is in the tens place, the digit 2 is in the hundreds place, the digit 7 is in the tenths place, and the digit 8 is in the hundredths place.The
position of each digit in the decimal place value chart is significant because it determines its value and magnitude. Moving one place to the left of the decimal point decreases the value of the digit by a factor of 10, while moving one place to the right increases the value of the digit by a factor of 10.Here
are some examples of decimal numbers and their corresponding place values:
- The number 0.5 has a 5 in the tenths place.
- The number 3.14 has a 4 in the tenths place, a 1 in the hundredths place, and a 3 in the ones place.
- The number 10.25 has a 1 in the tens place, a 0 in the ones place, a 2 in the tenths place, and a 5 in the hundredths place.
The relationship between place value and the size of the digit is straightforward. The place value determines whether the digit represents a larger or smaller quantity. Digits in higher place values, such as the ones or tens place, have a greater impact on the overall value of the number than digits in lower place values, such as the tenths or hundredths place.In
summary, the decimal place value system is based on the concept that each digit’s position in a number determines its value. The position of each digit in the chart is significant as it determines its value and magnitude. Understanding the relationship between place value and the size of the digit is crucial for comprehending and working with decimal numbers.
Reading and Writing Decimal Numbers Using the Chart: Decimal Place Value Chart Printable

Decimal numbers are a fundamental part of the number system, and understanding how to read and write them is essential. The decimal place value chart provides a visual representation that helps us identify the value of each digit in a decimal number.
Let’s explore how to read and write decimal numbers using this chart.To read a decimal number using the chart, we start from the left and move towards the right. Each digit represents a specific value based on its position in the chart.
The first digit to the left of the decimal point is the ones place, followed by the tenths place, hundredths place, thousandths place, and so on. The value of each digit is determined by multiplying it by the corresponding place value.For
example, let’s consider the decimal number 3.25. The digit 3 is in the ones place, so its value is simply 3. The digit 2 is in the tenths place, so its value is 2 multiplied by 0.1, which equals 0.2. The digit 5 is in the hundredths place, so its value is 5 multiplied by 0.01, which equals 0.05. Therefore, the decimal number 3.25 can be read as “three and twenty-five hundredths.”When
writing decimal numbers using the chart, we must place the decimal point accurately. The decimal point separates the whole number part from the fractional part. It is crucial to position the decimal point correctly to convey the intended value of the decimal number.For
instance, let’s take the decimal number 0.75. The digit 7 is in the tenths place, and the digit 5 is in the hundredths place. Placing the decimal point after the digit 7 indicates that the number is less than one.
Therefore, 0.75 can be written as “zero and seventy-five hundredths.”Using the decimal place value chart correctly ensures accurate representation and comprehension of decimal numbers. It allows us to understand the value of each digit and interpret decimal numbers with precision.
Examples of Reading and Writing Decimal Numbers Using the Chart
- Decimal number: 7.89
- Reading: “seven and eighty-nine hundredths”
- Writing: “seven and eighty-nine hundredths”
- Decimal number: 0.0064
- Reading: “zero and six thousand four hundredths”
- Writing: “zero and six thousand four hundredths”
- Decimal number: 2.5
- Reading: “two and five tenths”
- Writing: “two and five tenths”
Remember to always pay attention to the position of the decimal point and the corresponding place values when reading and writing decimal numbers using the chart. This will ensure clear and accurate communication of the intended value.
Comparing and Ordering Decimal Numbers
Decimal numbers can be compared and ordered using the decimal place value chart. This chart helps us understand the value of each digit in a decimal number and allows us to easily compare and order them.To compare decimal numbers using the decimal place value chart, we start by comparing the digits at the leftmost place value and move towards the right.
We compare the digits one by one, starting from the leftmost place value, until we find a difference.Here’s the process of comparing digits at each place value from left to right:
- Start by comparing the digits at the leftmost place value (usually the ones place).
- If the digits are the same, move to the next place value towards the right and compare the digits at that place value.
- Continue this process until you find a difference in the digits at a particular place value.
- The number with the greater digit at that place value is greater than the other number.
- If all the digits are the same up to the last decimal place, the numbers are equal.
Let’s look at an example to understand how to compare and order decimal numbers using the chart:Example 1:Consider the decimal numbers 3.14 and 3.
141. We compare the digits at each place value
- At the ones place, both numbers have the digit 3, so we move to the next place value.
- At the tenths place, both numbers have the digit 1, so we move to the next place value.
- At the hundredths place, the first number has the digit 4, while the second number has the digit 1. Since 4 is greater than 1, the first number (3.14) is greater than the second number (3.141).
Therefore, we can conclude that 3.14 > 3.141.In comparing decimal numbers, we use inequality symbols ( <, >, =) to indicate the relationship between the numbers. Here’s how we use these symbols:If the first number is greater than the second number, we use the “>” symbol. For example, 3.14 > 3.141.- If the first number is less than the second number, we use the “<" symbol. For example, 2.5 < 2.7. - If the two numbers are equal, we use the "=" symbol. For example, 0.75 = 0.75. By using the decimal place value chart and comparing digits at each place value, we can easily compare and order decimal numbers. This helps us understand the relative values of decimal numbers and make comparisons in various mathematical operations.
Adding and Subtracting Decimal Numbers Using the Chart

To add and subtract decimal numbers using the decimal place value chart, it is important to align the digits based on their place values.
If you have kids who love Spiderman, why not surprise them with some coloring pages featuring their favorite superhero? You can find printable coloring pages online, such as the ones available at coloring pages spiderman printable . These coloring pages are not only a great way to keep your kids entertained, but they also help improve their fine motor skills and creativity.
You can print out different Spiderman-themed coloring pages and let your kids unleash their imagination by coloring them. It’s a simple yet enjoyable activity that your kids will surely love.
The decimal place value chart helps in organizing the numbers and makes it easier to perform calculations accurately.When adding decimal numbers using the chart, follow these steps:
- Start by aligning the decimal points of the numbers being added.
- Add the digits in the rightmost place value column (ones).
- If the sum of the digits is greater than or equal to 10, regroup the digits by carrying over the excess to the next place value column (tenths).
- Repeat the process for each subsequent place value column, carrying over any excess digits as necessary.
- Once all the digits have been added, write the sum with the decimal point in the same position as the original numbers.
For example, let’s add 2.35 and 1.27 using the decimal place value chart:“` 2.35+ 1.27
——
“`Start by aligning the decimal points:“` 2.35+ 1.27
——
“`Add the digits in the rightmost column (ones): 5 + 7 =
Since the sum is greater than or equal to 10, regroup the digits:
“` 2.35+ 1.27
——
2“`Carry over the 1 to the next column (tenths) and continue adding:“` 2.35+ 1.27
——
12“`Finally, write the sum with the decimal point in the same position as the original numbers: 3.62.When subtracting decimal numbers using the chart, the process is similar to addition. However, instead of carrying over digits, you may need to borrow from the next place value column.For
example, let’s subtract 4.56 from 8.91 using the decimal place value chart:“` 8.91
- 4.56
- ——
“`Start by aligning the decimal points:“` 8.91
If you’re looking for some fun activities to entertain your guests during the Christmas season, why not try playing Christmas trivia games? You can find printable versions of these games online, like the ones available at christmas trivia games printable . These games are a great way to test everyone’s knowledge about Christmas traditions, history, and popular culture.
You can divide your guests into teams and see who can answer the most questions correctly. Not only will it be a fun and interactive activity, but it will also create a festive atmosphere at your gathering.
- 4.56
- ——
“`Subtract the digits in the rightmost column (ones): 1
- 6 =
- Since the difference is negative, borrow 1 from the next column:
“` 8.91
- 4.56
- ——
11“`Subtract the borrowed 1 from 9 and continue subtracting:“` 8.91
- 4.56
- ——
5“`Finally, write the difference with the decimal point in the same position as the original numbers: 4.35.In both addition and subtraction, regrouping and carrying over digits is important to ensure accurate calculations. The decimal place value chart provides a visual representation of the numbers and their place values, making it easier to perform these operations.
Practice using the chart to add and subtract decimal numbers to improve your skills in working with decimals.
Multiplying and Dividing Decimal Numbers Using the Chart
When multiplying or dividing decimal numbers, the decimal place value chart can be a helpful tool to ensure accuracy and maintain the correct placement of the decimal point in the result.To multiply decimal numbers using the chart, follow these steps:
- Align the numbers vertically with the decimal points in line.
- Multiply the numbers as if they were whole numbers, disregarding the decimal points.
- Count the total number of decimal places in both numbers.
- Place the decimal point in the product, counting from the right, according to the total number of decimal places obtained in step 3.
For example, let’s multiply 3.2 by 0.5 using the decimal place value chart: 3.2x 0.5
—–
16 (multiply 2 by 5, ignoring the decimal points)+ 0 (multiply 3 by 0)
—–
1.6 (place the decimal point one place from the right, as there is one decimal place in total)To divide decimal numbers using the chart, follow these steps:
- Align the numbers vertically with the decimal points in line.
- Divide the numbers as if they were whole numbers, disregarding the decimal points.
- Count the total number of decimal places in both numbers.
- Place the decimal point in the quotient, counting from the right, according to the total number of decimal places obtained in step 3.
For example, let’s divide 4.8 by 0.6 using the decimal place value chart: 4.8÷ 0.6
—–
8 (divide 4 by 6, disregarding the decimal points)
—-
8.0 (place the decimal point one place from the right, as there is one decimal place in total)Remember, when multiplying or dividing decimal numbers using the chart, it is important to align the digits correctly and count the decimal places accurately to ensure the correct placement of the decimal point in the result.
Practical Applications of Decimal Place Value Chart
Understanding the decimal place value system is essential in various real-life scenarios. It provides a framework for accurately representing and manipulating decimal numbers. Let’s explore some practical applications where the decimal place value chart plays a crucial role.
Financial Transactions
- When managing personal finances, understanding decimal place value is vital. Whether it’s budgeting, calculating expenses, or tracking savings, decimal numbers are commonly used.
- In banking, decimal place value is crucial for accurate transactions. From calculating interest rates, loan payments, to currency conversions, the chart helps ensure precise calculations.
- Businesses rely on decimal place value for various financial operations such as inventory management, pricing products, and calculating profits.
Measurements
- In the field of science, decimal place value is utilized to measure quantities such as length, volume, mass, and temperature. The chart helps in accurate conversions between different units.
- In construction and engineering, decimal place value is essential for precise measurements, ensuring buildings and structures are built to exact specifications.
- Cooking and baking often involve measurements in decimal form. The chart assists in following recipes accurately and scaling ingredients accordingly.
Data Analysis and Statistics, Decimal place value chart printable
- Decimal place value is fundamental in data analysis and statistics. It allows for precise representation and comparison of numerical data.
- When analyzing financial data, decimal place value helps in calculating percentages, averages, and other statistical measures.
- In scientific research, decimal place value is crucial for recording and analyzing experimental results, ensuring accuracy in scientific findings.
Accuracy in Practical Applications
Accurate use of the decimal place value chart is of utmost importance in practical applications. Even a small error in decimal placement can lead to significant miscalculations or misleading conclusions. Maintaining precision ensures financial transactions are correct, measurements are accurate, and data analysis is reliable.
Conclusion
The decimal place value chart finds practical applications in various aspects of our daily lives, from financial transactions to measurements and data analysis. Understanding and utilizing the chart accurately is crucial for precise calculations and reliable results.
